About Photomasks for Semiconductors
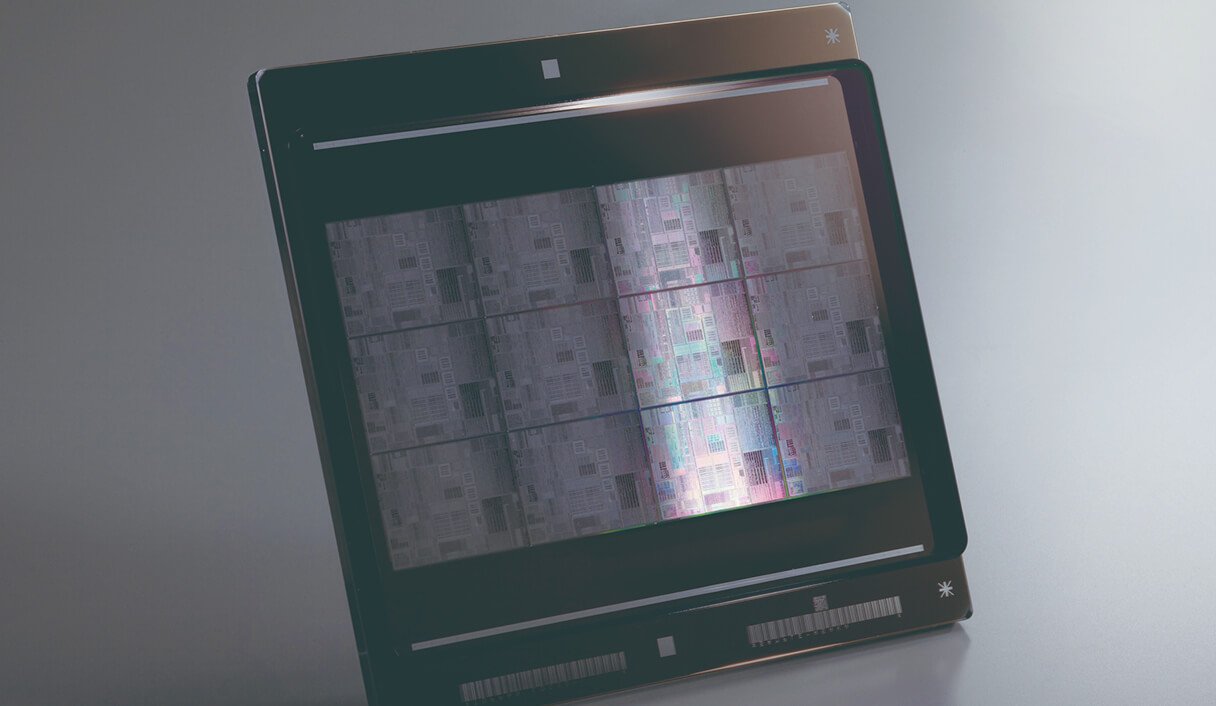
Photomasks play an important role in the semiconductor manufacturing process and are the master plates used to transfer circuits onto semiconductor wafers. Based on the design data, an electron beam is used to create an electronic circuit pattern on a photomask substrate (mask blank), which is then etched with chemicals, stripped of photoresist (photosensitive material), cleaned, measured, and inspected before the completed photomask is ready for production.
Types of Photomasks for Semiconductors
Binary Masks
The structure of a binary mask is simple; it is a photomask blank covered with patterned layer of opaque material. Its transmission characteristics are either transparent or non-transparent. A Binary mask is used for building a pattern in which line width is larger than the exposure wave length.
Tekscend Photomask and its blanks vendor have co-developed new types of binary blanks with superior workability (OMOG: Opaque MoSi on Glass). We have managed to create blanks for binary masks with better CD performance and higher resolution.
Phase Shift Masks
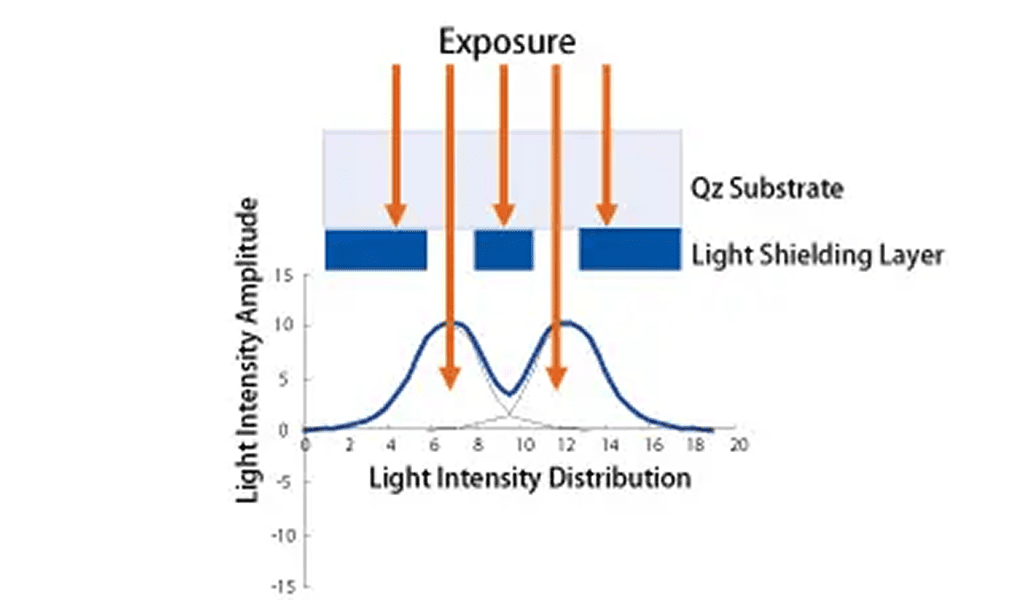
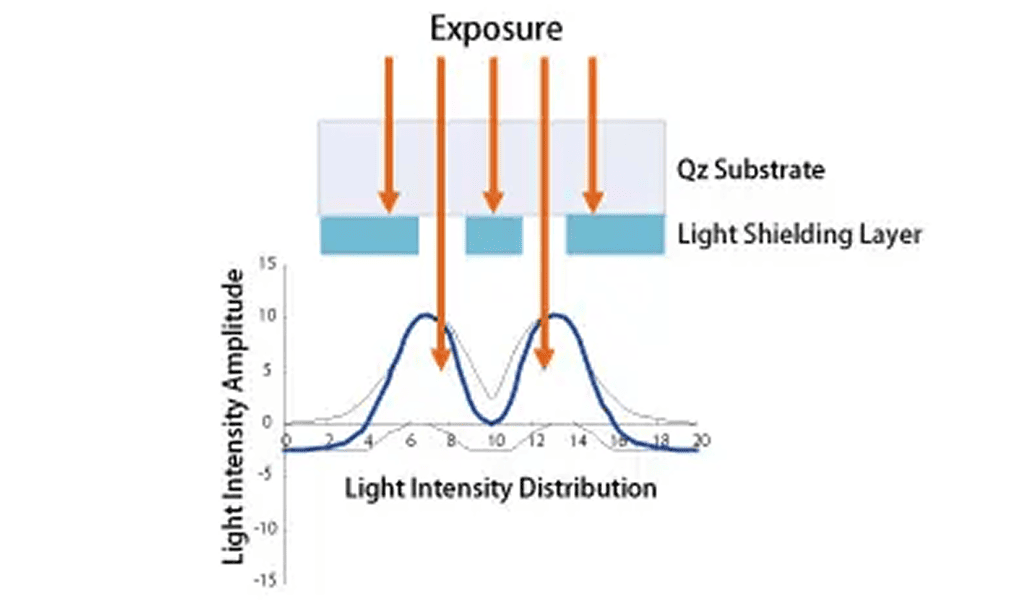
Phase-shifting masks (PSM) achieve improved wafer printability with higher resolution and increased DOF (Depth of Focus), by controlling the phase shift and the transmission rate of the light transmission through the photomask. This is a standard technology for lithography in which line width being printed is smaller than the exposure wave length.
Most well known PSM photomasks are called Halftone masks (Attenuated PSM) and Levenson masks (Alternating PSM).
EUV Photomasks
EUV lithography is the newest generation of lithography technique. Unlike conventional DUV lithography that use transmissive photomasks, EUV lithography requires the use of reflective photomasks for patterning circuits.